Introduction
In PostgreSQL, retrieving precise data is often more important than retrieving all data. The WHERE clause is the SQL feature that allows you to filter rows based on conditions, ensuring that queries return only the information you need. Whether you’re selecting records, updating values, or deleting entries, mastering the WHERE clause is essential for efficient database management.
What is the WHERE Clause in PostgreSQL?
The WHERE clause in PostgreSQL is a conditional filter applied to SQL statements. It restricts the rows returned by a query, updated by an operation, or deleted from a table.
If you’re new to PostgreSQL, I’d recommend starting with Installation, and Add PostgreSQL to Path Windows and below articles before you learn how to query tables.
- Connect to PostgreSQL Database Server Using psql and pgAdmin
- Load PostgreSQL Sample Database: Beginner-Friendly Tutorial
- PostgreSQL SELECT Clause Explained – Syntax, Examples, Best Practices for Querying Data
PostgreSQL WHERE Clause Syntax for Filtering Rows
👉 This syntax defines which columns to retrieve, from which table, and under what condition.
👉 The WHERE clause is used in conjunction with the SELECT command. Before filtering data, ensure you are mastering the SELECT statement basics with our high-performance querying masterclass.
SELECT column_list
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;- SELECT column_list → Columns to display.
- FROM table_name → Table source.
- WHERE condition → Boolean expression that determines which rows qualify.
PostgreSQL WHERE Clause Examples
Under the PostgreSQL WHERE clause examples, you’ll find practical queries that demonstrate how to filter rows using different SQL operators and conditions. From simple equality checks to combining multiple conditions with AND and OR, these examples show how to refine results for precise data retrieval. You’ll also learn how to use the IN operator to match multiple values, apply the LIKE operator for pattern matching, and leverage the BETWEEN operator for range filtering. Finally, examples of excluding values with the NOT EQUAL operator highlight how PostgreSQL WHERE clause can be applied to SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements for efficient query optimization.
PostgreSQL WHERE Clause with Equality Condition to Filter Rows
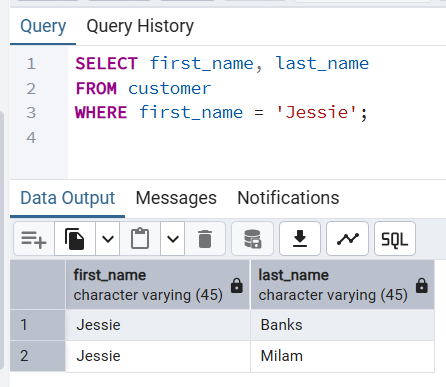
👉 Returns only those customer whose first name is Jessie.
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM customer
WHERE first_name = 'Jessie';Output
first_name | last_name
------------+-----------
Jessie | Banks
Jessie | Milam
(2 rows)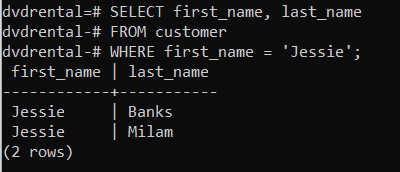
PostgreSQL WHERE Clause with Multiple Conditions Using AND Operator
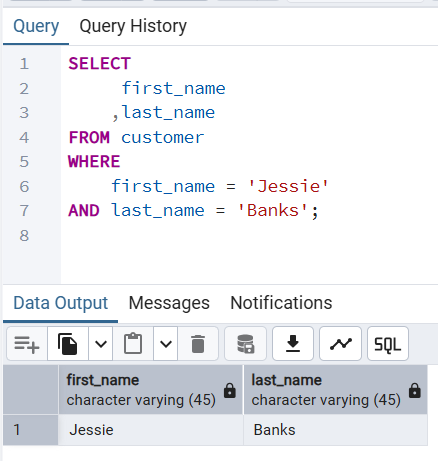
👉 Retrieves customer whose first name is Jessie and last name is Banks.
SELECT
first_name
,last_name
FROM customer
WHERE
first_name = 'Jessie'
AND last_name = 'Banks';Output
first_name | last_name
------------+-----------
Jessie | Banks
(1 row)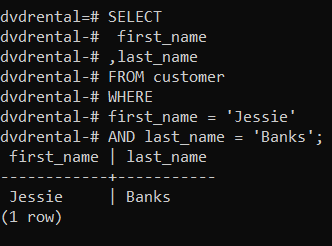
PostgreSQL WHERE Clause with OR Operator for Alternative Matches
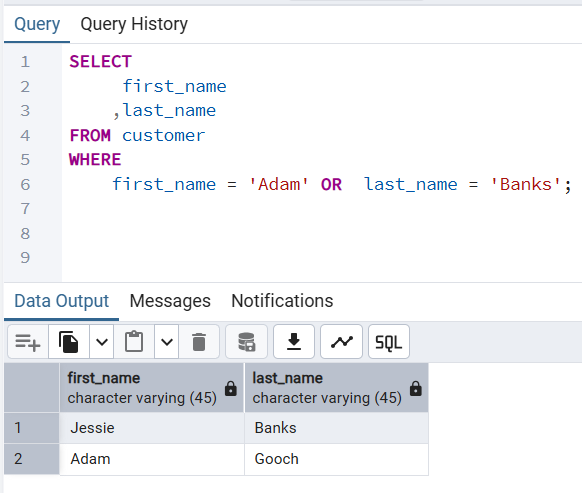
👉 Results customer if there first name is Adam OR their last name is Banks.
SELECT
first_name
,last_name
FROM customer
WHERE
first_name = 'Adam'
OR last_name = 'Banks';first_name | last_name
------------+-----------
Jessie | Banks
Adam | Gooch
(2 rows)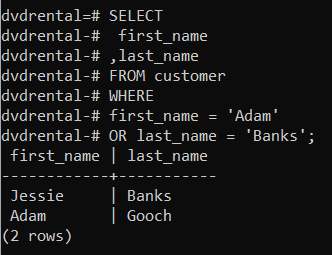
PostgreSQL WHERE Clause Using IN Operator to Match Multiple Values
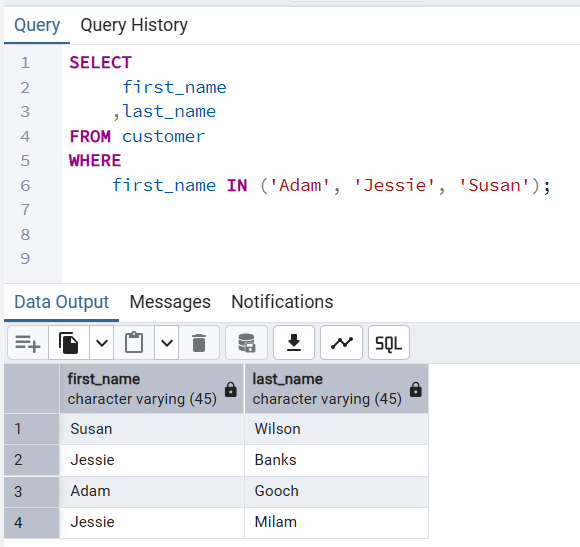
👉 Results customer whose first name is Adam, Jessie, and Susan.
SELECT
first_name
,last_name
FROM customer
WHERE
first_name IN ('Adam', 'Jessie', 'Susan'); first_name | last_name
------------+-----------
Susan | Wilson
Jessie | Banks
Adam | Gooch
Jessie | Milam
(4 rows)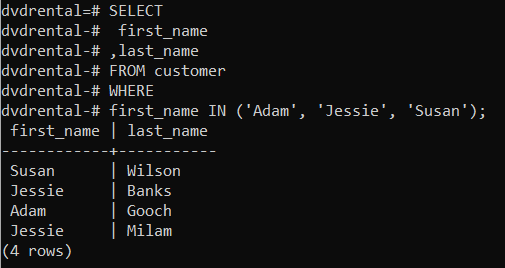
PostgreSQL WHERE Clause with LIKE Operator for Pattern Matching
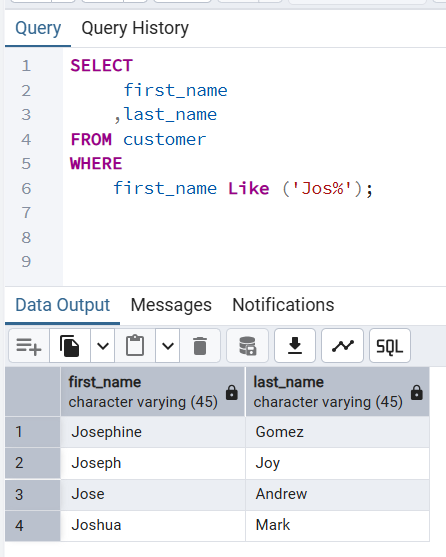
👉 Results customers whose first name starts with the following characters Jos.
SELECT
first_name
,last_name
FROM customer
WHERE
first_name Like ('Jos%'); first_name | last_name
------------+-----------
Josephine | Gomez
Joseph | Joy
Jose | Andrew
Joshua | Mark
(4 rows)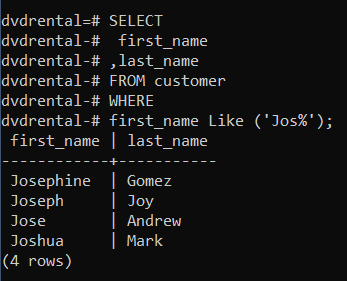
PostgreSQL WHERE Clause with BETWEEN Operator for Range Filtering
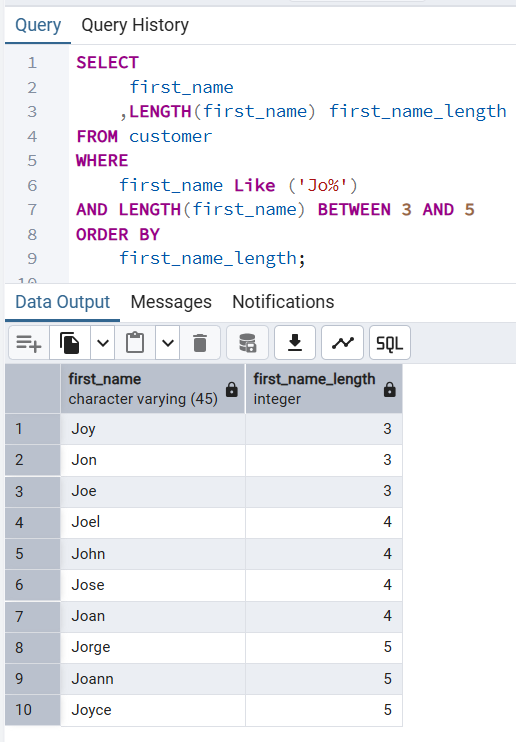
👉 Retrieves all customers whose first names starts with “Jo%” and whose first name contains three to five characters and to find this we use the BETWEEN operator. The advantage of using a BETWEEN operator is that it will return true if a value is found to be in the range of values specified and, in our case, it is between three to five characters.
SELECT
first_name
,LENGTH(first_name) first_name_length
FROM customer
WHERE
first_name Like ('Jo%')
AND LENGTH(first_name) BETWEEN 3 AND 5
ORDER BY
first_name_length;first_name | first_name_length
------------+-------------------
Joy | 3
Jon | 3
Joe | 3
Joel | 4
John | 4
Jose | 4
Joan | 4
Jorge | 5
Joann | 5
Joyce | 5
(10 rows)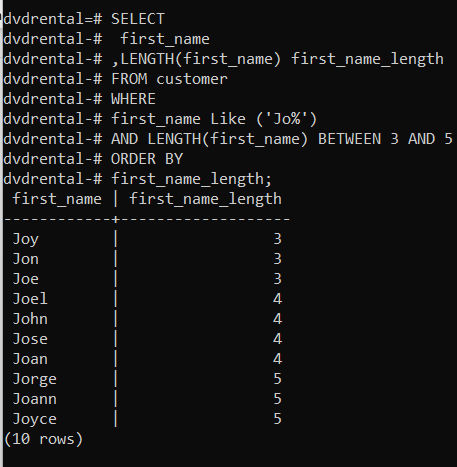
PostgreSQL WHERE Clause Excluding Values Using NOT EQUAL Operator
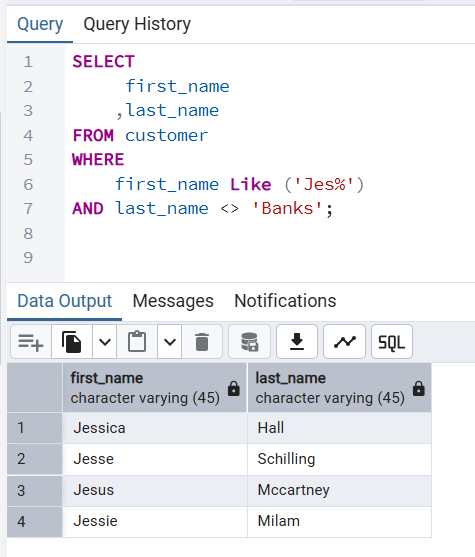
👉 Returns all customers whose first name starts as Jes and whose last name is not banks.
SELECT
first_name
,last_name
FROM customer
WHERE
first_name Like ('Jes%')
AND last_name <> 'Banks';first_name | last_name
------------+-----------
Jessica | Hall
Jesse | Schilling
Jesus | Mccartney
Jessie | Milam
(4 rows)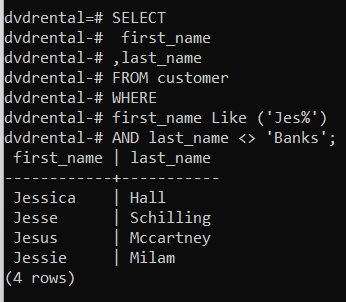
Performance Tips for PostgreSQL WHERE Clause
- Use indexes to speed up WHERE clause queries.
- Avoid wrapping indexed columns in functions (e.g., LOWER(column)), as it prevents index usage.
- Combine logical operators (AND, OR, NOT) carefully to avoid unnecessary scans.
- Use EXPLAIN to analyze query execution plans.
Conclusion
The PostgreSQL WHERE clause is the backbone of precise data retrieval. By applying conditions, you can filter rows, update specific records, or delete targeted entries without affecting the entire dataset. This improves both performance and accuracy in SQL queries.
Next Steps
- Learn advanced operators like IS NULL, NOT IN, and EXISTS.
- Explore JOINs with WHERE clauses for multi-table filtering.
- Practice writing queries with complex conditions to build confidence.
- Optimize queries using EXPLAIN to understand execution plans.
📌 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) PostgreSQL WHERE Clause Tutorial with Examples
Question 1: What is the purpose of the WHERE clause in PostgreSQL? The WHERE clause filters rows based on conditions, ensuring only relevant data is returned.
Question 2: Can I use WHERE with UPDATE and DELETE statements? Yes, WHERE can restrict which rows are updated or deleted, preventing unintended changes.
Question 3: How does the LIKE operator work in PostgreSQL WHERE clause? LIKE allows pattern matching. For example, WHERE name LIKE ‘A%’ finds names starting with “A”.
Question 4: What is the difference between WHERE and HAVING in PostgreSQL? WHERE filters rows before grouping, while HAVING filters groups after aggregation.
Question 5: Does the WHERE clause affect query performance? Yes, especially on large tables. Proper indexing can significantly improve performance.
Question 6: Can I combine multiple conditions in a WHERE clause? Absolutely. Use logical operators like AND, OR, and NOT to build complex conditions.
More PostgreSQL Articles and Tips
- PostgreSQL Row Count for All Tables: 7 Fastest Methods
- Mastering PostgreSQL Index-Only Scans: 40x Speed for Heavy Queries
- PostgreSQL Performance Tuning: The “Golden Ratios” for Memory Configuration
- PostgreSQL SELECT Clause: A Masterclass in High-Performance Querying & Best Practices
- PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE Tutorial with Examples and Best Practices

Add comment