Introduction
Learning how to connect to PostgreSQL database server using psql andhow to connect to PostgreSQL database server using pgAdmin is one of the first steps for beginners working with PostgreSQL. Whether you prefer the command line (psql) or a graphical interface (pgAdmin), this tutorial will guide you through both methods with clear, beginner‑friendly instructions.
👉 If you haven’t installed PostgreSQL yet, check out our article Install PostgreSQL on Windows: Step‑by‑Step Beginner’s Guide before continuing.
🔹 Tools You’ll Use for Connecting
When you install PostgreSQL, two essential tools are included:
- psql – a terminal‑based utility for direct SQL execution.
- pgAdmin – a web‑based graphical tool for managing PostgreSQL databases.
Both are widely used, and knowing how to use them ensures you can connect to PostgreSQL in any environment.
Connect to PostgreSQL Database Server Using psql (Command Line)
The PostgreSQL psql command line connection is fast and powerful.
Step 1: Open your terminal or command prompt
- Windows → Command Prompt
- Linux/macOS → Terminal
Step 2: Run the psql command
psql -U postgres- psql → starts the interactive terminal.
- -U postgres → specifies the user account (default is postgres).
Step 3: Enter your password
You’ll be prompted for the password you set during installation. Once authenticated, you’ll see the PostgreSQL prompt:
postgres=#Step 4: Check PostgreSQL version
SELECT version();version
------------------------------------------------------------
PostgreSQL 18.1 on x86_64-windows, compiled by msvc-19.44.35219, 64-bit
(1 row)This confirms your connection and shows the installed PostgreSQL version.
Step 5: View current database
SELECT current_database();------------------
postgres
(1 row)Step 6: Check host and port details
SELECT inet_server_addr(), inet_server_port();inet_server_addr | inet_server_port
------------------+------------------
127.0.0.1 | 5432
(1 row)👉 This method is perfect for developers who want direct access to SQL commands and database management.
Connect to PostgreSQL Database Server Using pgAdmin (Graphical Interface)
The PostgreSQL pgAdmin connection tutorial is ideal for beginners who prefer a GUI.
Step 1: Launch pgAdmin
Open pgAdmin from your Start menu or applications list. It will run in your web browser.
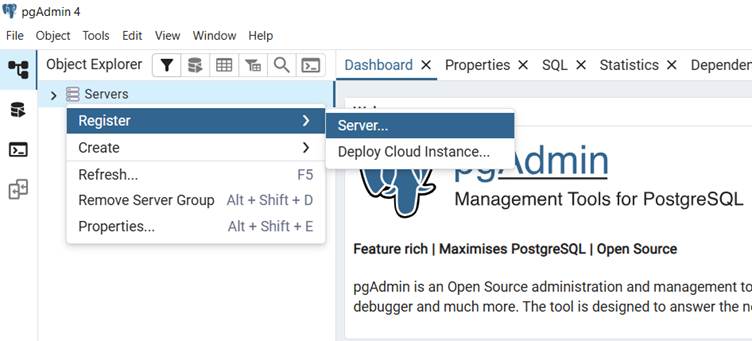
Step 2: Register a new server
- Right‑click on Servers → Register > Server…
- Provide a name (e.g., Local).
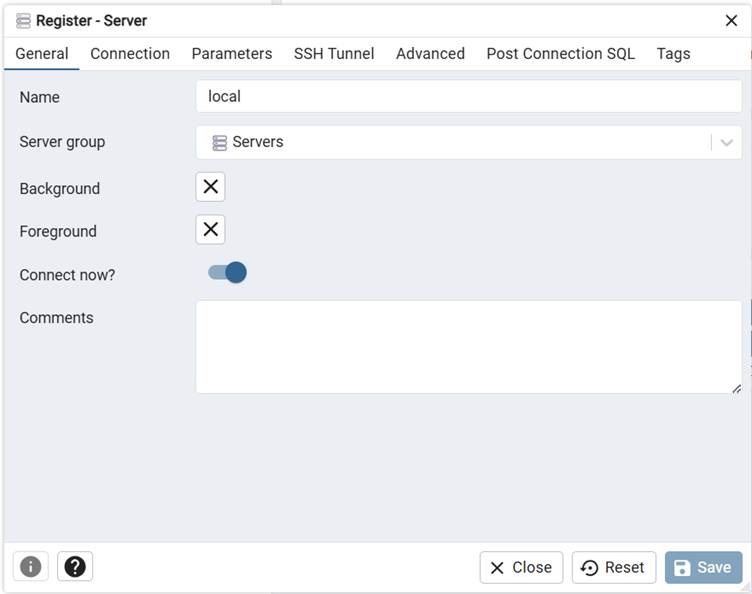
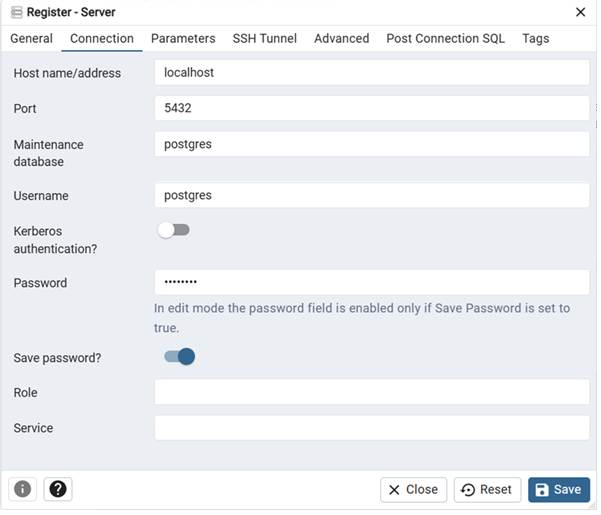
Step 3: Configure connection settings
- Host:
localhost - Username:
postgres - Password: your installation password
- Save the configuration.
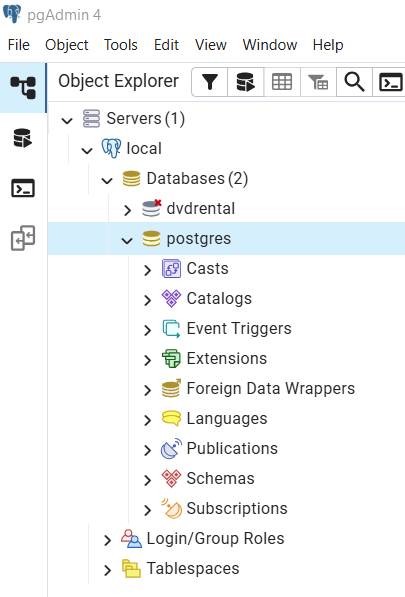
Step 4: Expand the server node
By default, PostgreSQL includes a database named postgres.
Step 5: Open the Query Tool
Navigate to Tools > Query Tool.
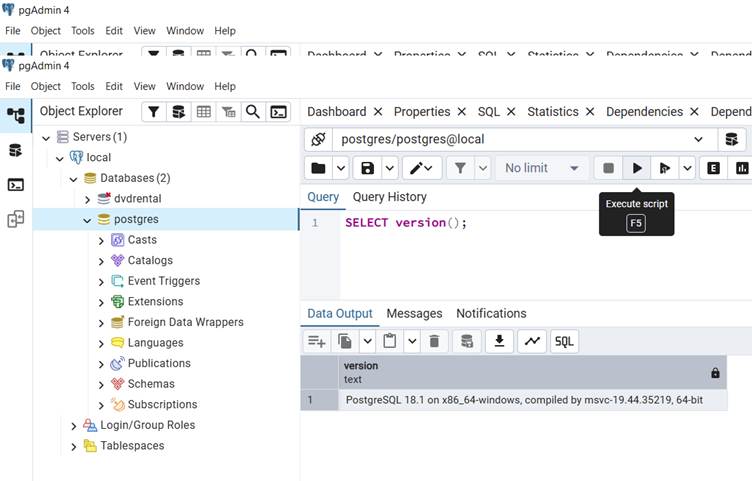
Step 6: Run SQL queries
Type your SQL commands in the editor and click Execute. Results will appear in the output panel.
👉 Beginners often find pgAdmin easier since it provides a user‑friendly interface for managing databases, tables, and queries.
Why Learn Both Methods?
- psql command line connection → Fast, lightweight, and ideal for scripting.
- pgAdmin connection tutorial → Visual, intuitive, and beginner‑friendly.
Mastering both ensures you can work efficiently in any environment.
👉 For advanced tutorials, see our guides on Connecting PostgreSQL with Python, Connecting PostgreSQL with Java, and PostgreSQL Remote Connections.
Conclusion
Connecting to PostgreSQL doesn’t have to be complicated. Whether you use the psql interactive terminal or the pgAdmin application, both methods give you full access to your PostgreSQL database server. Beginners should start with pgAdmin for ease of use, but learning psql is essential for advanced tasks and automation.
By following this guide, you now know how to connect to PostgreSQL database server using psql and pgAdmin, check your version, view databases, and run queries. With these skills, you’re ready to explore PostgreSQL further and build powerful applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) How to Connect to a PostgreSQL Database Server
1. How do I connect to PostgreSQL using psql?
Open your terminal, run psql -U postgres, enter your password, and you’ll be connected to the PostgreSQL database server using psql.
2. How do I connect to PostgreSQL using pgAdmin?
Launch pgAdmin, register a new server, enter host, username, and password, then expand the server node and use the Query Tool to run SQL commands.
3. What is the default PostgreSQL database?
The default PostgreSQL database is named postgres, created automatically during installation.
4. How do I check the PostgreSQL version?
Run SELECT version(); in either psql or pgAdmin.
5. What is the default PostgreSQL port?
PostgreSQL uses port 5432 by default. Confirm with SELECT inet_server_port();.
6. Can I connect to PostgreSQL remotely?
Yes. Configure pg_hba.conf and postgresql.conf to allow external connections, then use the server’s IP and port.
7. How do I reset the PostgreSQL password?
ALTER USER postgres WITH PASSWORD ‘newpassword’;
8. Can I connect PostgreSQL to programming languages like Python or Java?
Yes. PostgreSQL supports connections via drivers such as psycopg2 for Python and JDBC for Java. See our PostgreSQL Python Connection Guide and PostgreSQL Java Connection Guide.
More PostgreSQL Articles and Tips
- PostgreSQL Row Count for All Tables: 7 Fastest MethodsDiscover how to bypass slow SELECT COUNT(*) scans in PostgreSQL. This guide provides 7 high-performance methods—including metadata queries and original PL/pgSQL scripts—to get precise and estimated row counts for all database tables efficiently.
- Mastering PostgreSQL Index-Only Scans: 40x Speed for Heavy QueriesPostgreSQL Index‑Only Scan is a powerful technique to boost query performance by eliminating unnecessary heap fetches. By leveraging the Visibility Map, developers can reduce I/O overhead and achieve up to 40x speed improvements in heavy workloads. Covering Indexes ensure queries are satisfied directly from the index, making PostgreSQL performance tuning more effective. If your PostgreSQL query is slow despite having an index, updating the visibility map and optimizing select queries can deliver dramatic gains. Learn how to reduce heap fetches, compare index‑only scan vs index scan, and master database optimization for large datasets.
- PostgreSQL Performance Tuning: The “Golden Ratios” for Memory ConfigurationGeneric tuning formulas often fail because they ignore the underlying hardware abstraction layer. In this deep-dive, I breaks down the “Golden Ratios” for PostgreSQL memory management. Learn why shared_buffers strategy differs between Bare Metal and AWS Aurora, how to calculate work_mem to prevent production OOM kills, and get an exclusive buffer cache hit ratio script to diagnose your bottlenecks in real-time. Whether you are scaling for high concurrency or optimizing a massive 128GB RAM instance, these battle-tested strategies ensure your database stays fast and resilient.
- PostgreSQL SELECT Clause: A Masterclass in High-Performance Querying & Best PracticesMaster the PostgreSQL SELECT clause with this deep-dive guide. Learn how to optimize queries, leverage index-only scans for 40x speed gains, and avoid common production bottlenecks like ‘SELECT *’. Includes a 1M-row performance lab
- PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE Tutorial with Examples and Best PracticesLearn PostgreSQL CREATE TABLE with schema, IF NOT EXISTS, constraints, inheritance, multiple foreign keys, and temporary tables. Includes examples and best practices for developers.

Add comment