Discover this step‑by‑step beginner’s guide to easily install PostgreSQL on Windows 11.
Discover this How to Restore PostgreSQL Sample Database dvdrental on PostgreSQL Server Using pgAdmin.
Set Up a PostgreSQL Database on Windows: Setting Windows PATH for Postgres Tools
When working with PostgreSQL on Windows, one of the most important steps is configuring the system so that you can easily access Postgres utilities from any terminal. If you’re wondering how to set Windows PATH for Postgres tools, the process involves updating your environment variables so that commands like psql can be run directly without navigating to the installation folder. By setting Windows PATH for Postgres tools, developers streamline workflows and avoid repetitive navigation.
For users on the latest operating system, learning how to add PostgreSQL to Path Windows 11 is especially useful, though the same approach applies if you want to add PostgreSQL to PATH Windows on earlier versions. You can also add PostgreSQL to path command line by editing environment variables directly, ensuring that the PostgreSQL Path Windows is recognized system-wide. This configuration is part of managing PostgreSQL Environment Variables Windows, which allows your database tools to be accessible globally. In short, once you add PostgreSQL to path, you’ll have a smoother experience setting up and managing your PostgreSQL database on Windows.
Configuring the PostgreSQL Bin Directory in Windows PATH
To run PostgreSQL utilities like psql or pg_restore from any location in the command prompt, you need to configure the PATH environment variable.
This is done by linking the PostgreSQL bin directory to Windows PATH, which removes the need to manually navigate to the installation folder each time you want to use Postgres tools.
The first step is to locate the bin folder inside your PostgreSQL installation directory. On most Windows setups, this directory is created automatically during installation and contains all the essential executables. Once identified, you can add it to the PATH so that PostgreSQL commands are recognized system‑wide.
For example, if you install PostgreSQL 18, the path to the bin directory will look like this
C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\18\binSteps to Access Environment Variables in Windows
Step 1: Use the Windows key + R shortcut to launch the Run command window.
Step 2: Enter sysdm.cpl in the text field and hit Enter. This will open the System Properties panel.
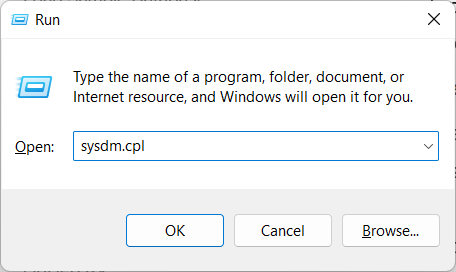
Step 3: Navigate to the Advanced settings tab, then choose the Environment Variables option to proceed.

Understanding Environment Variables in Windows
When the Environment Variables window opens, it displays two distinct areas: one labeled User variables (specific to your Windows account) and another called System variables (applies to all users on the machine).
If your goal is to make PostgreSQL tools available system‑wide (recommended), you should modify the PATH variable under the System variables section.
However, if you prefer to configure access only for your individual account (Personal Use), you can update the PATH within the User variables section instead.
Editing the PATH Variable in User Settings
At this stage, highlight the PATH entry located within the User variables section. Once selected, choose the Edit option to modify it. This allows you to add the PostgreSQL bin directory so commands like psql can be executed directly from the Windows command line.
Adding a New Path Entry
In the Edit Environment Variables dialog, choose the New option to insert an additional entry. This step allows you to include the PostgreSQL bin directory so that Postgres commands are recognized directly from the Windows command prompt without extra navigation.
Adding PostgreSQL Bin Directory to PATH
Next, type in the full directory location for PostgreSQL, for example: C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\18\bin
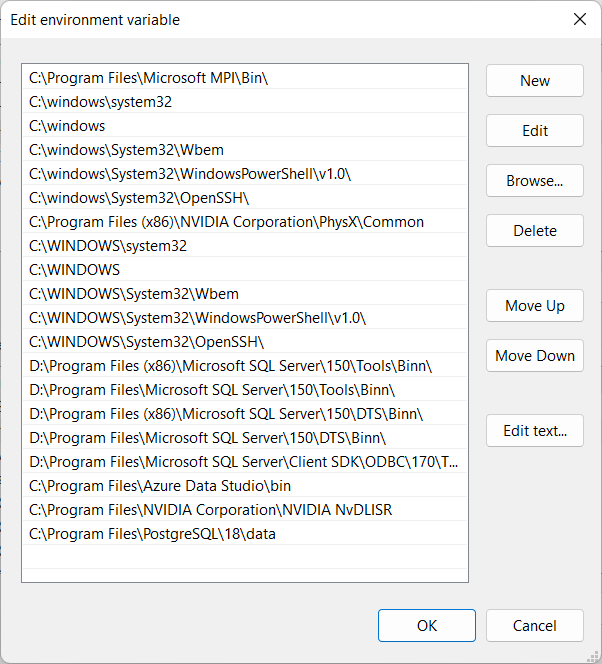
After entering the path, confirm by selecting OK. This action ensures the PostgreSQL bin folder is successfully appended to the PATH environment variable, allowing commands like psql and pg_restore to run from any command prompt window in Windows.
Saving Changes to Environment Variables
To complete the configuration, confirm your updates by selecting OK in the Environment Variables dialog. Then, apply the changes by pressing OK again in the System Properties window. This ensures the new PostgreSQL PATH settings are stored and recognized across Windows.
Completion Message
Well done — the PostgreSQL database server is now fully set up on your Windows machine. With the installation complete, you can begin managing databases, running SQL commands, and using PostgreSQL tools directly from the command line.
More PostgreSQL Articles and Tips
- Install PostgreSQL on Windows: Step‑by‑Step Beginner’s GuideLearn how to install PostgreSQL on Windows with this beginner friendly tutorial. Step by step instructions for downloading, configuring, and setting up PostgreSQL, pgAdmin, and command line tools.
- Add PostgreSQL to PATH on Windows (Step-by-Step Guide)Learn step by step how to set Windows PATH for Postgres tools. Easily add PostgreSQL to PATH Windows 11, configure PostgreSQL environment variables Windows, and run Postgres from the command line.
- Connect to PostgreSQL Database Server Using psql and pgAdminLearn how to connect to PostgreSQL database server using psql command line and pgAdmin GUI. Easy tutorial for beginners with queries, host/port setup, and FAQs.
- Load PostgreSQL Sample Database: Beginner-Friendly TutorialLearn how to load the PostgreSQL DVD Rental sample database using pgAdmin. Step-by-step beginner’s guide to creating, restoring, and exploring PostgreSQL databases for practice.
- PostgreSQL SELECT Clause: The Complete Guide (with Performance Tips)Master the PostgreSQL SELECT statement with this beginner-friendly tutorial. Learn syntax, examples, and best practices for querying data efficiently.

Add comment